|
Beginning geometry |
|
|
|
To use the resources of this chapter you must first register |
|
|
CONTENTS |
|
|
ITEM |
|
TYPE |
|
NUMBER |
|
| Starting geometry |
|
Workout |
|
36 slides |
|
| Starting geometry |
|
Library |
|
13 questions |
|
|
|
Once you have registered, you can work through the slides one by one.
The workout comprises a series of sides that guide you systematically through the topic concept by concept, skill by skill. The slides may be used with or without the support of a tutor. The methodology is based on problem-solving that advances in logical succession by concept and difficulty. The student is presented with a problem or series of questions, and the next slide presents the fully-worked solution. To use the material you must sign-in or create an account.
blacksacademy.net comprises a complete course in mathematics with resources that are comprehensive.
|
|
|
|
SAMPLE FROM THE WORKOUT |
| Showing American English version |
SLIDE 1 - EXPLANATION |
 |
|
SLIDE 2 - QUESTION 1 |
 |
|
|
SAMPLE FROM THE LIBRARY |
| Showing American English version |
QUESTION [difficulty 0.1] |
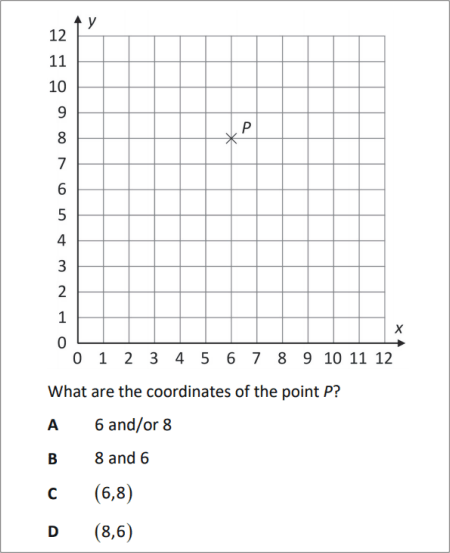 |
|
SOLUTION |
 |
|
|
DEPENDENCIES |
|
|
|
|
CONCEPTS |
|
|
|
|
LEV. |
|
|
Point
|
|
390.1 |
|
|
Coordinate
|
|
390.1 |
|
|
Components (horizontal and vertical)
|
|
390.1 |
|
|
Vertex (implicit)
|
|
390.2 |
|
|
Coordinates of vertices of a rectangle
|
|
390.2 |
|
|
Vertices of a polygon
|
|
390.4 |
|
|
Drawing (mapping) vertices to shape
|
|
390.6 |
|
|
Line segment
|
|
391.0 |
|
|
Shortest distance between two points
|
|
391.0 |
|
|
Line
|
|
391.0 |
|
|
Straight
|
|
391.0 |
|
|
Plotting a point
|
|
391.1 |
|
|
Parallel
|
|
391.5 |
|
|
Perpendicular
|
|
391.5 |
|
|
Parallel lines
|
|
391.6 |
|
|
Same distance apart
|
|
391.6 |
|
|
Angle
|
|
391.6 |
|
|
Right-angle
|
|
391.7 |
|
|
Average
|
|
392.0 |
|
|
Mid-point
|
|
392.0 |
|
|
Triangle
|
|
392.3 |
|
|
Equilateral triangle
|
|
392.3 |
|
|
Isosceles triangle
|
|
392.3 |
|
|
Right-angled triangle
|
|
392.3 |
|
|
Scalene triangle
|
|
392.3 |
|
|
Combinatoric problems on triangles
|
|
392.6 |
|
|
Regular or irregular polygon (implicit)
|
|
392.8 |
|
|
Regular pentagon
|
|
392.8 |
|
|
Hexagon, regular hexagon
|
|
393.0 |
|
|
Octogon, regular octogon
|
|
393.2 |
|
|
|
|
RAW CONTENT OF THE WORKOUT |
|
| To make use of this chapter, please first register. Then you can work through the slides one by one. |
|
| What is provided here is the raw text of the workout. Most of the information is contained in the image files, which are not included with this text. The text may appear deceptively short. (The content overall of blacksacademy.net is vast.) Any in-line questions appear as a question mark [?]. This text is provided only as an indication of the overall quantity of material contained in the chapter. To use the material you must sign-in or create an account. |
|
| * |
|
|
Coordinate geometry
SLIDE 1
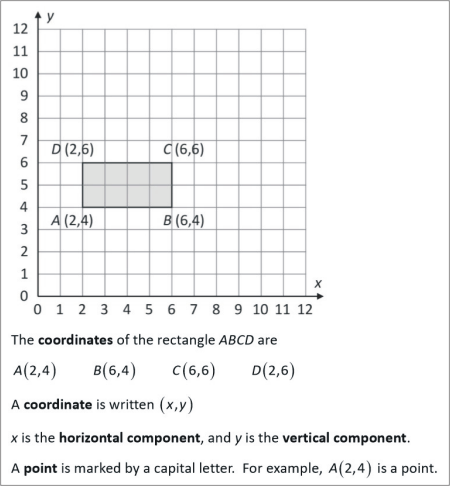
The coordinates of the rectangle ABCD are
A coordinate is written
x is the horizontal component, and y is the vertical component.
A point is marked by a capital letter. For example, is a point.
SLIDE 2
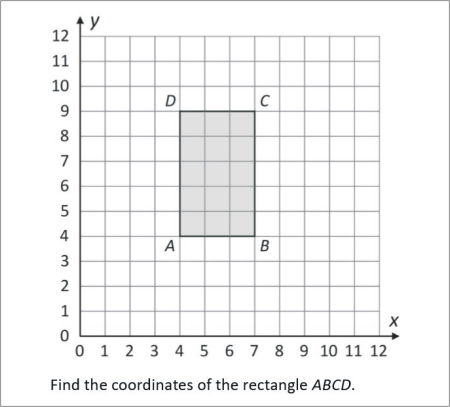
Find the coordinates of the rectangle ABCD.
SLIDE 3
SLIDE 4
Find the coordinates of the triangle ABC and of the four-pointed star PQRSTUVW.
SLIDE 5
SLIDE 6
Draw the shape with coordinates
SLIDE 7
SLIDE 8
Draw the shape with coordinates
SLIDE 9
SLIDE 10
A line segment is the shortest distance between two points.
A line is the path that goes in the same direction both ways as a line segment.
Lines look straight.
SLIDE 11
Example
Plot the line segment joining to .
A point is plotted on a graph by making a sharp cross, here shown in red, so that the cross lies exactly at the coordinate.
SLIDE 12
Plot the points .
Draw the line segment AB and draw the line passing through P and Q.
SLIDE 13
SLIDE 14
? Draw the lines AB, LM and PQ where
? Describe the relationship between the lines AB and LM.
? Describe the relationship between lines AB and PQ.
SLIDE 15
?
? AB and LM are parallel.
? AB and PQ are perpendicular.
SLIDE 16
Parallel lines
Two lines are parallel, if they are always the same distance apart.
A pair of parallel lines is marked with arrows
Angles
When two lines intersect they make an angle.
SLIDE 17
Two parallel lines are crossed by a third line, l.
The angles marked a and b are equal.
The crossing line is perpendicular to the two parallel lines.
The angle is a right-angle.
A right-angle is shown by a square.
SLIDE 18
State whether the following are true of false
? AB is parallel to CD
? AB is perpendicular to HG
? HG is parallel is CD
? IJ is perpendicular to KL
? EF is parallel to KL
? CD is perpendicular to EF
SLIDE 19
State whether the following are true of false
? AB is parallel to CD ? true
? AB is perpendicular to HG ? true
? HG is parallel is CD ? false, they are perpendicular
? IJ is perpendicular to KL ? true
? EF is parallel to KL ? true
? CD is perpendicular to EF ? false
SLIDE 20
Example
Plot the line segment from to and find its midpoint.
The midpoint is found by taking the average of the x and y coordinates of the two points.
x coordinate of A is 2, x coordinate of B is 10. Average .
Average of the y coordinates .
Midpoint: .
SLIDE 21
? Plot the line segment from to and find its midpoint M.
? Plot the line segment from to and find its midpoint N.
? Plot the line segment from to and find its midpoint P.
SLIDE 22
? Midpoint of to is
? Midpoint of to is
? Midpoint of to is
SLIDE 23
Triangles
equilateral isosceles right-angled scalene
three equal sides two equal sides no equal sides
SLIDE 24
Classify these triangles
……………. ……………. ……………. …………….
……………. ……………. ……………. …………….
……………. ……………. ……………. …………….
SLIDE 25
isosceles scalene equilateral right-angled
scalene isosceles right-angled equilateral
scalene scalene right-angled isosceles
SLIDE 26
How many triangles?
SLIDE 27
SLIDE 28
A pentagon is any five-sided figure.
A regular pentagon is the five-sided symmetric figure where all sides are equal.
Find the perimeters of the pentagon and regular pentagon above.
SLIDE 29
Pentagon
Regular pentagon
SLIDE 30
A hexagon is any six-sided figure.
A regular hexagon is the six-sided symmetric figure where all sides are equal.
Find the perimeters of the hexagon and regular hexagon above.
SLIDE 31
Hexagon
Regular hexagon
SLIDE 32
An octagon is any eight-sided figure.
A regular octagon is the eight-sided symmetric figure where all sides are equal.
Find the perimeters of the octagon and regular octagon above.
SLIDE 33
Octagon
Regular octagon
|
|